High frequency of copy number imbalances in Rubinstein–Taybi
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Clinical exome sequencing identifies novel CREBBP variants in 18 Chinese Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome kids with high frequency of polydactyly - Yu - 2019 - Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine - Wiley Online Library
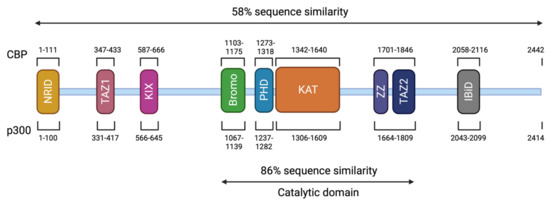
Genes, Free Full-Text

CNV profiles of Chinese pediatric patients with developmental disorders - ScienceDirect
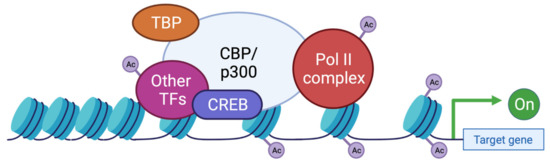
Genes, Free Full-Text
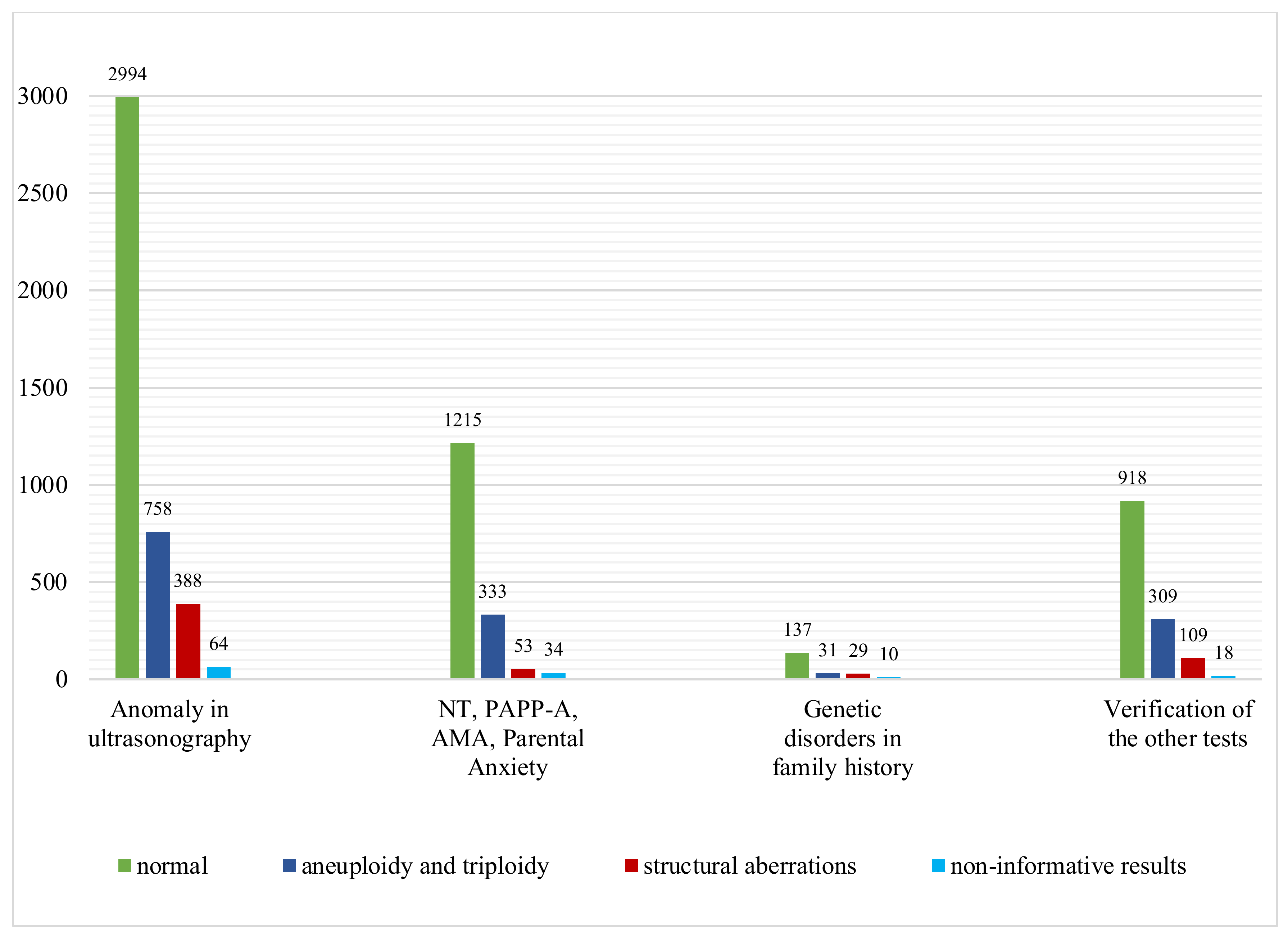
Genes, Free Full-Text
Frontiers De novo 8p21.3→ p23.3 Duplication With t(4;8)(q35;p21.3) Translocation Associated With Mental Retardation, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and Congenital Heart Defects: Case Report With Literature Review
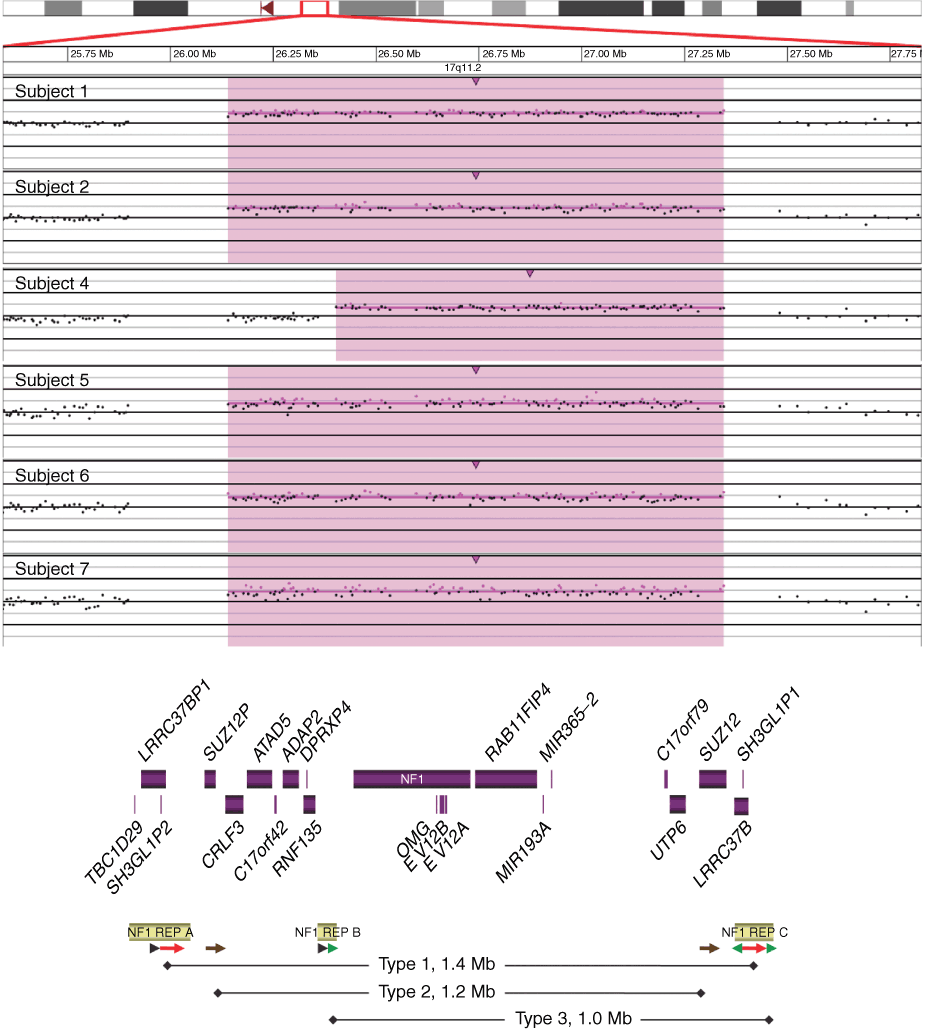
NF1 microduplications: identification of seven nonrelated individuals provides further characterization of the phenotype

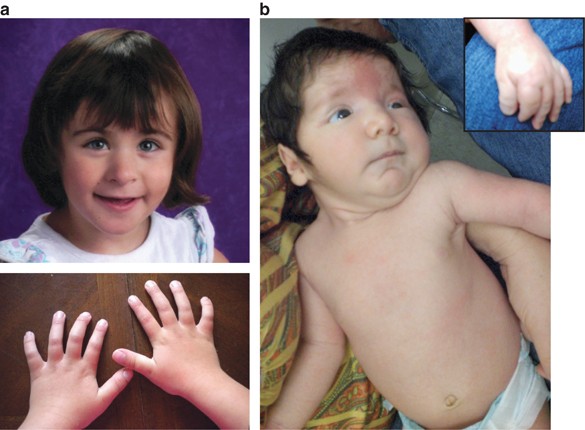
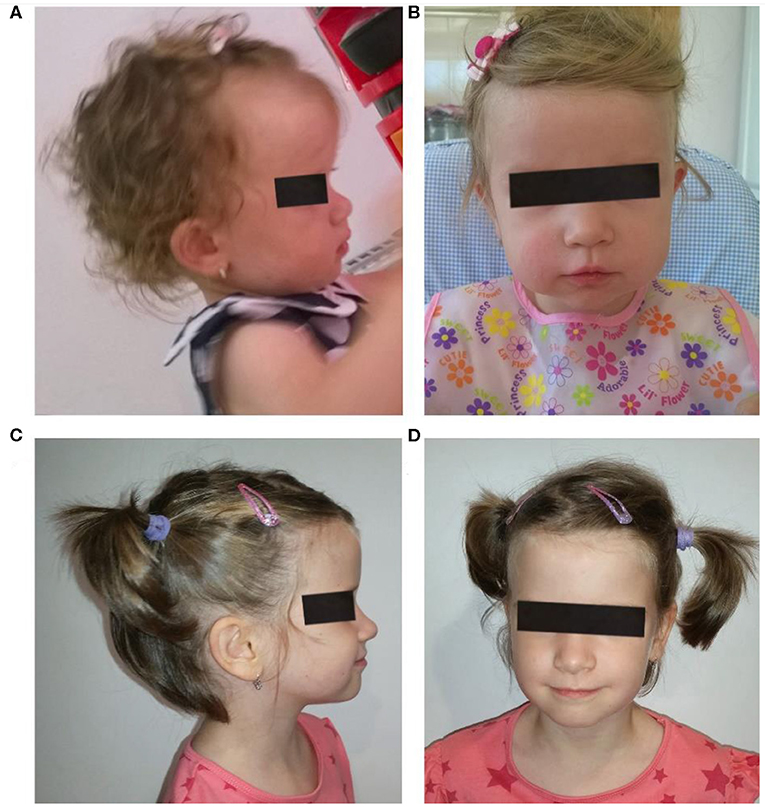
Clinical photos of the patients. (a) Case 1: Dysmorphic facial features
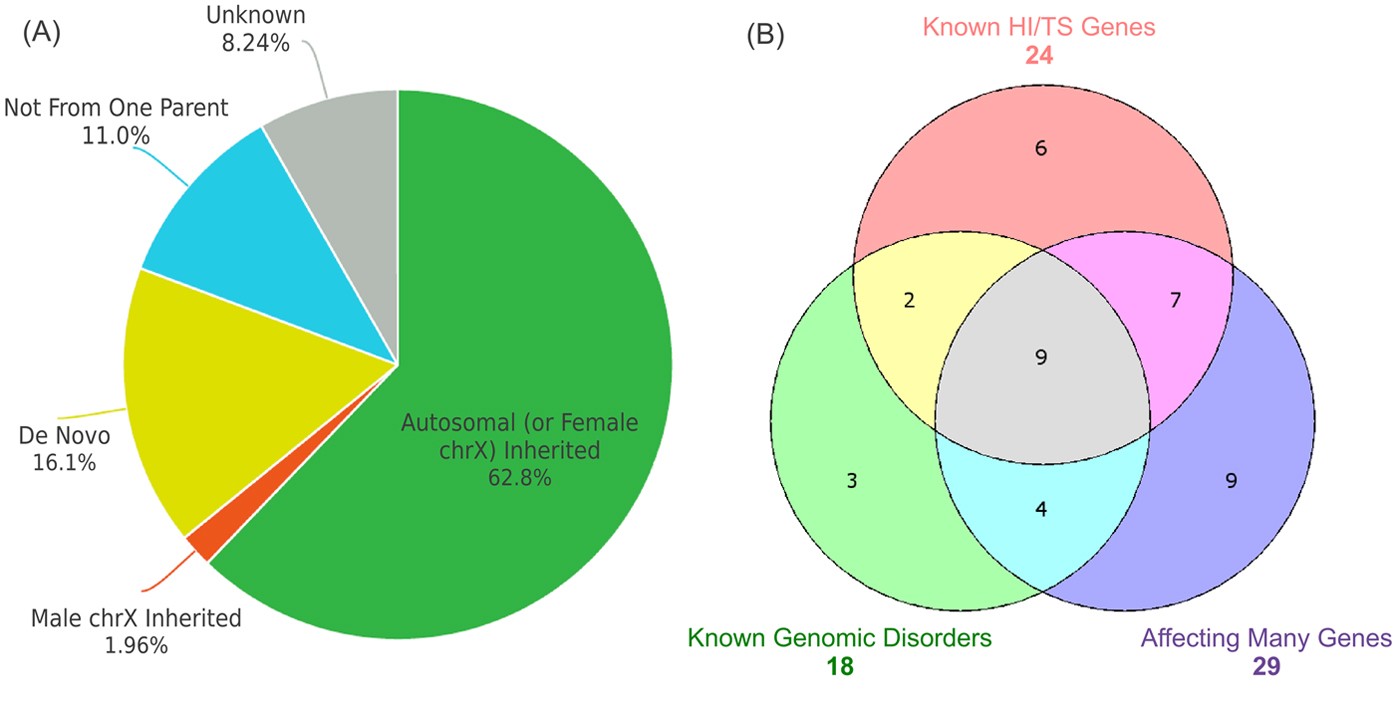
CNV analysis in Chinese children of mental retardation highlights a sex differentiation in parental contribution to de novo and inherited mutational burdens

PDF) Electroclinical phenotype in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome

Clinical exome sequencing identifies novel CREBBP variants in 18 Chinese Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome kids with high frequency of polydactyly - Yu - 2019 - Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine - Wiley Online Library

Clinical exome sequencing identifies novel CREBBP variants in 18 Chinese Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome kids with high frequency of polydactyly - Yu - 2019 - Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine - Wiley Online Library
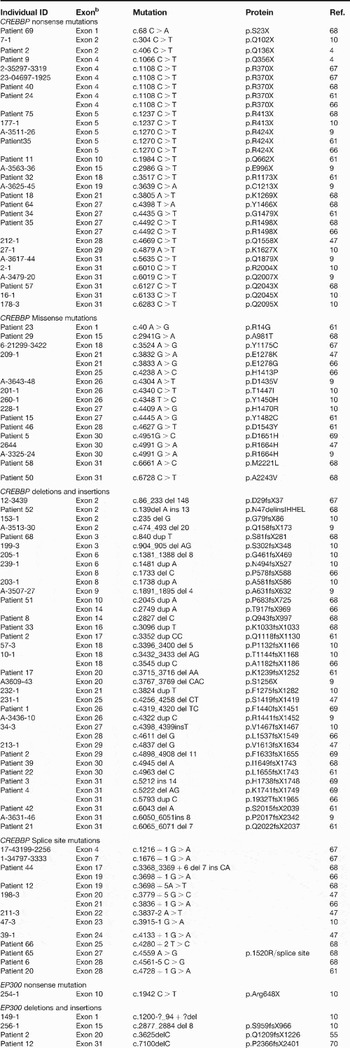
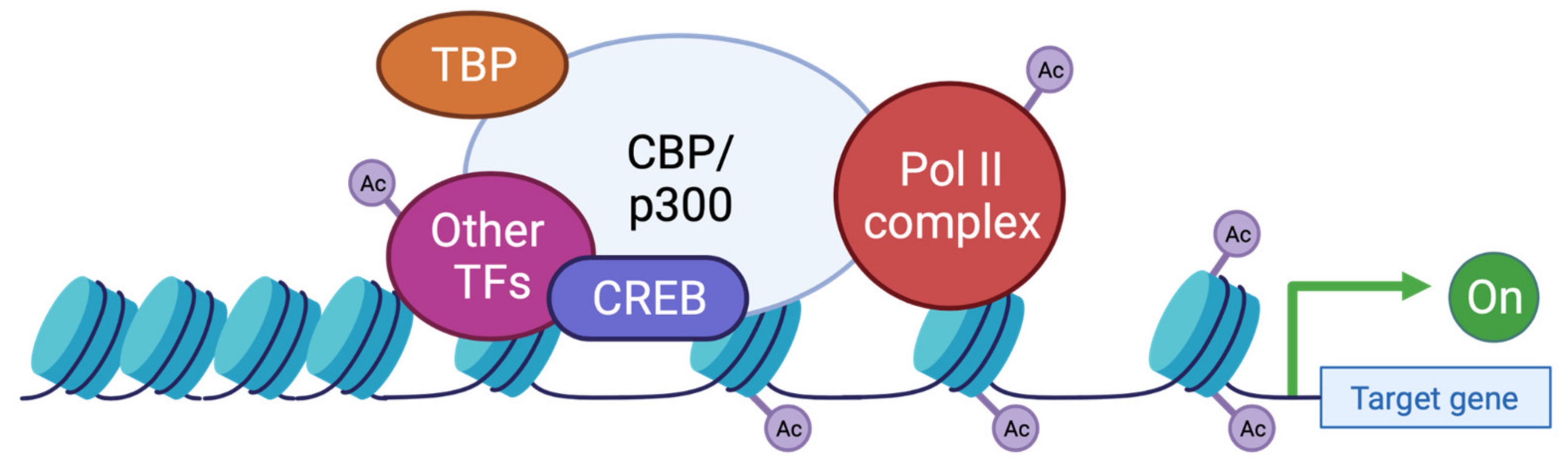
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: clinical and molecular overview, Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine
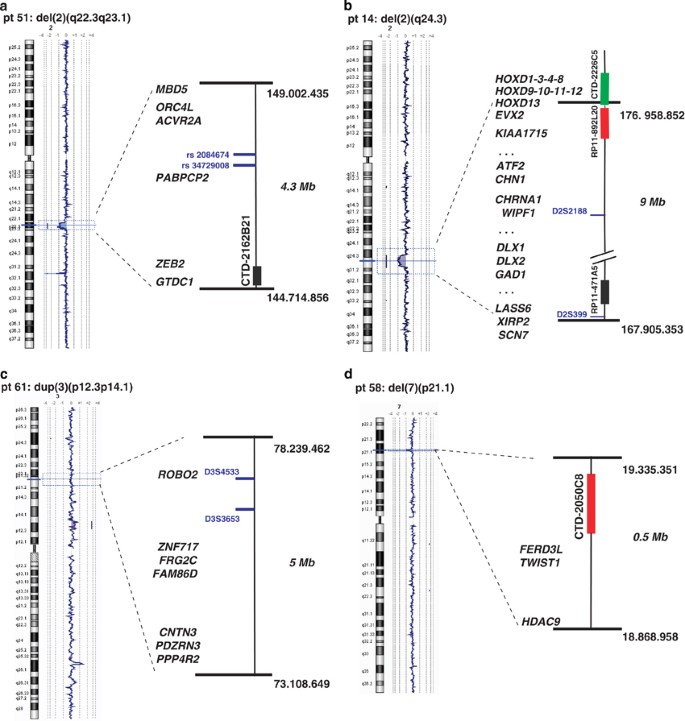
High frequency of copy number imbalances in Rubinstein–Taybi patients negative to CREBBP mutational analysis
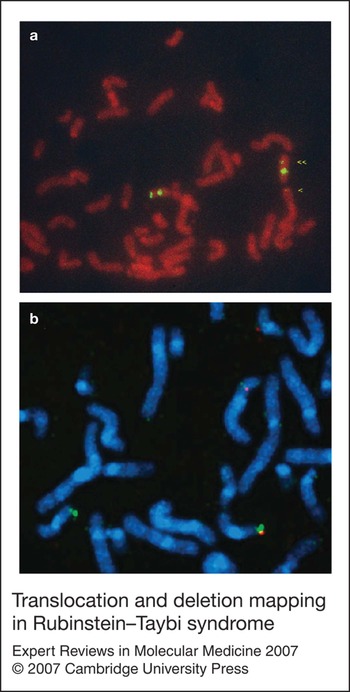
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: clinical and molecular overview, Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)