Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Acute chagasic encephalitis is a clinically severe central nervous system (CNS) manifestation. However, the knowledge of the nervous form of Chagas disease is incomplete. The role of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) on mice behavior and brain lesions induced by Trypanosoma cruzi (Colombian strain) was herein investigated in mice treated with the mAChR agonist and antagonist (carbachol and atropine), respectively. Immunosuppressed or non-immunosuppressed mice were intracerebroventricularly (icv) or intraperitoneally (ip) infected. All groups were evaluated 15 d.p.i. (days post infection). Intraperitoneally infected animals had subpatent parasitemia. Patent parasitemia occurred only in icv infected mice. The blockade of mAChR increased the parasitemia, parasitism and lesions compared to its activation. Infected not treated (INT ip) mice did not present meningitis and encephalitis, regardless of immunosuppression. INT icv brains presented higher cellularity, discrete signs of cellular degeneration, frequent presence of parasites and focal meningitis. The immunosuppressed atropine + icv mice presented increased intracellular parasitism associated with degenerative parenchymal changes, while carbachol + icv mice presented discrete meningitis, preservation of the cortex and absence of relevant parasitism. Cholinergic receptor blockage increased impairment of coordination vs. receptor activation. Muscarinic cholinergic pathway seems to be involved in immune mediated cell invasion events while its blockade favored infection evolution, brain lesions, and behavioral alterations.
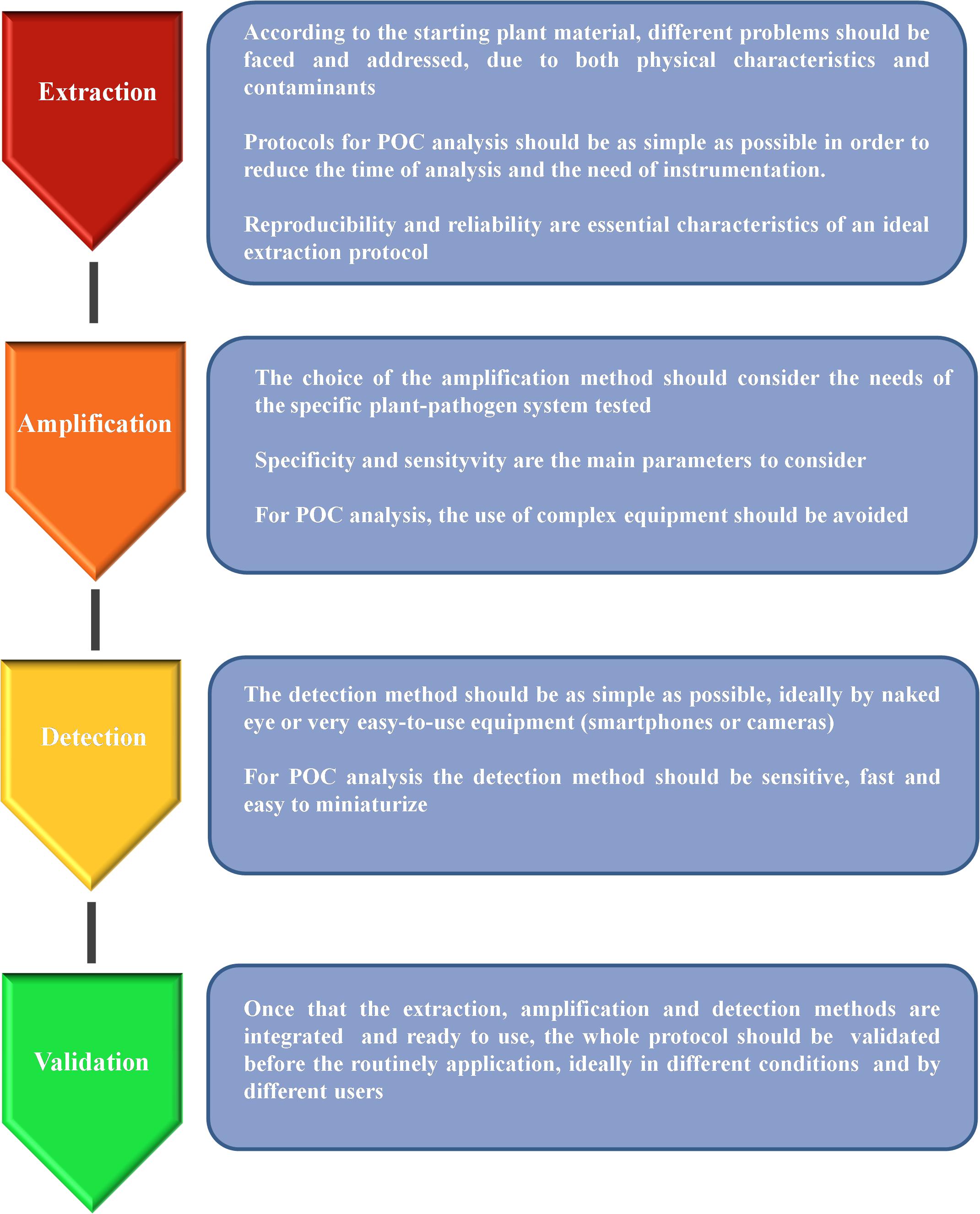
Frontiers Molecular Approaches for Low-Cost Point-of-Care Pathogen Detection in Agriculture and Forestry
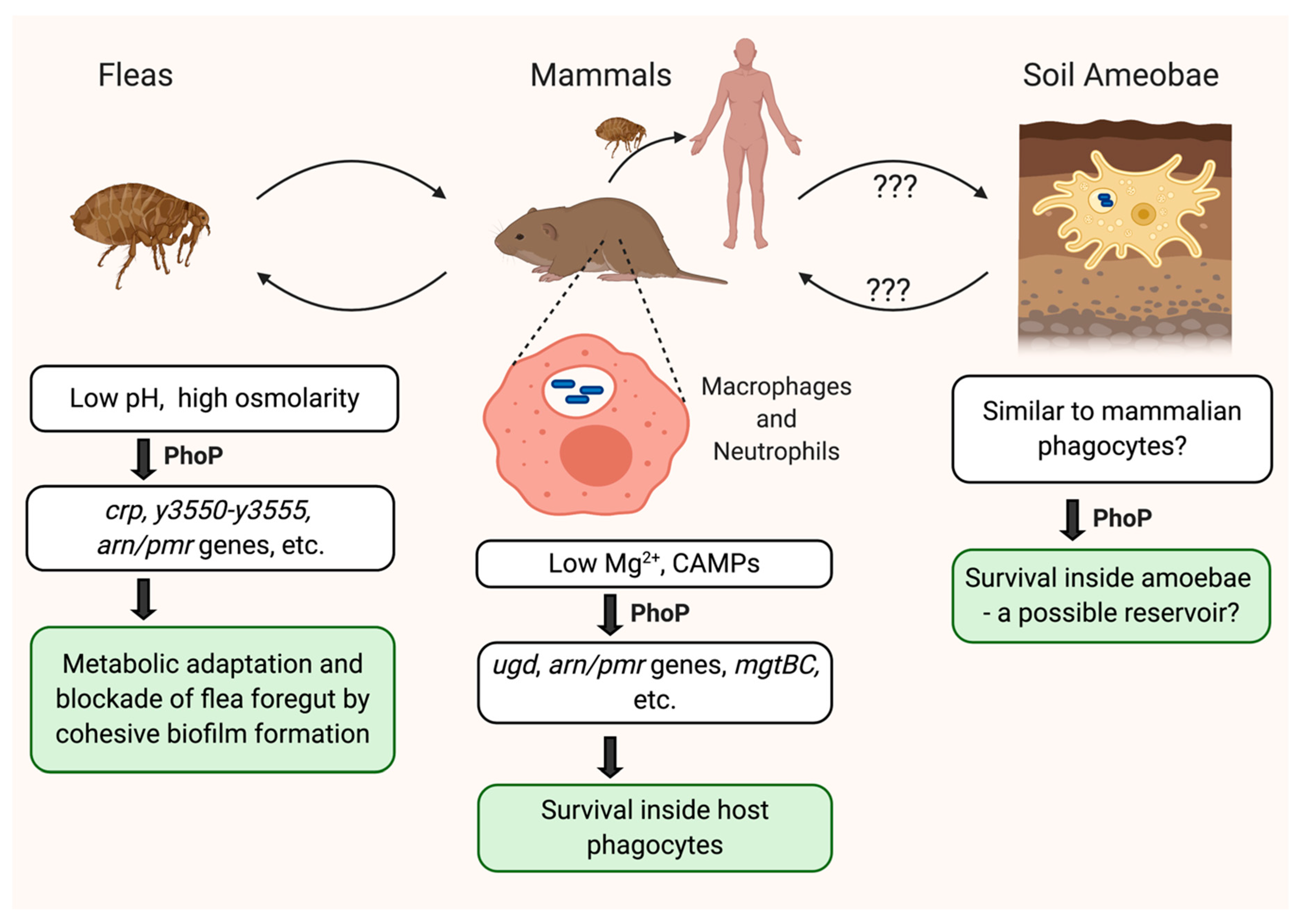
Yersinia pestis: Introduction and morphology - Overall Science
Evolution of pathogen tolerance and emerging infections: A missing experimental paradigm

Pathogenic bacteria - Wikipedia

A culture-free biphasic approach for sensitive and rapid detection of pathogens in dried whole-blood matrix
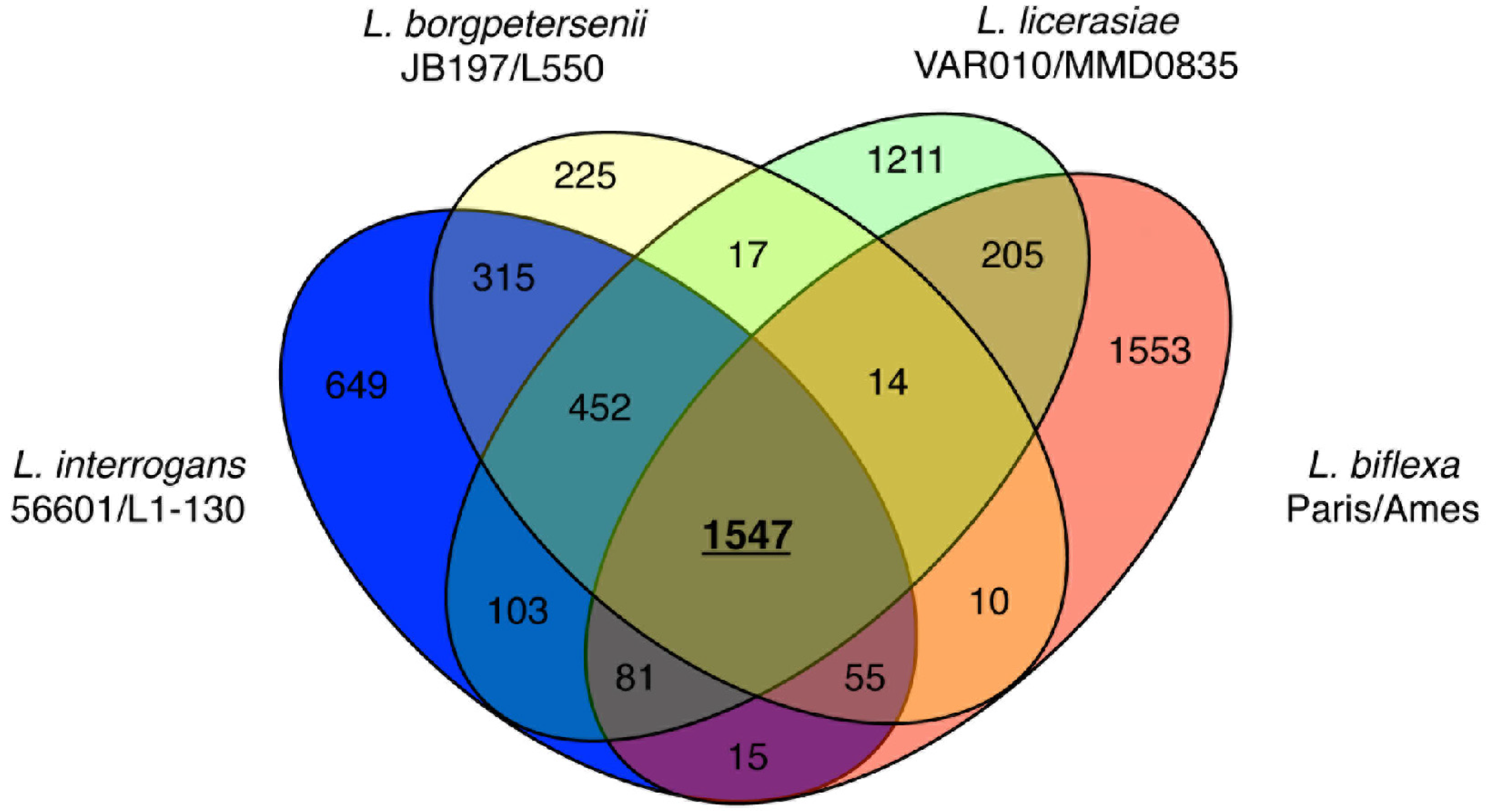
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Pathogens and Immunity
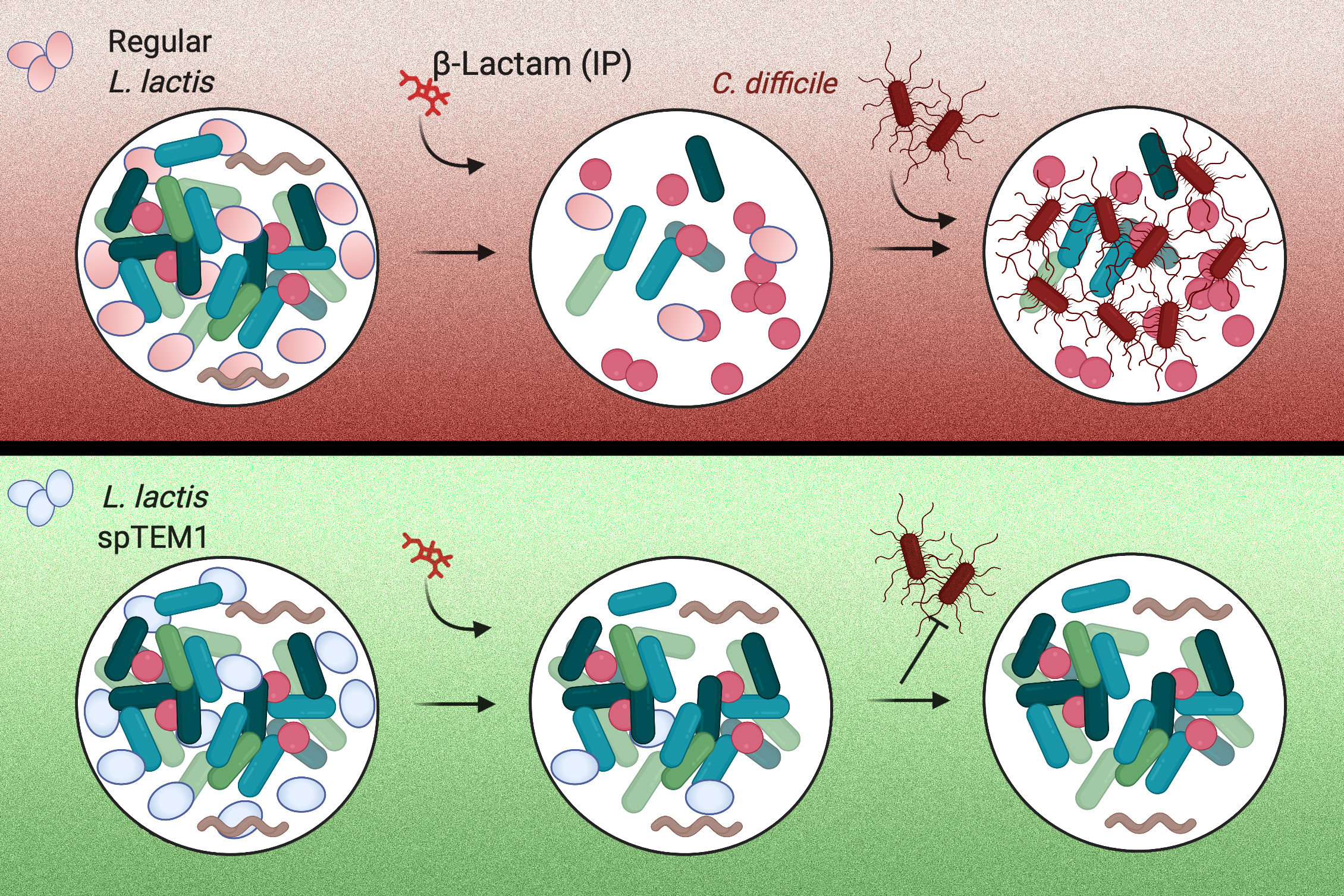
Engineered bacteria could help protect “good” gut microbes from antibiotics, MIT News

Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis - The Lancet
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)
.png)






